Tohoku Univ. Technology:Plant disease control agent containing a bacteriophage: T20-032
Easy to handle with a great effect on disease control!
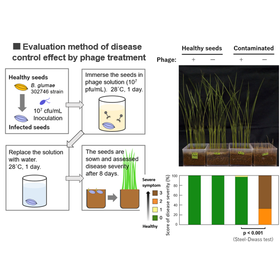
Burkholderia gulmae and B. plantarii are pathogenic bacteria and cause rice seedling rot which is one of the most serious problems in the process of raising seedlings for rice cultivation. The main method for controlling plant diseases is application of chemical pesticides. However, risks for emergence of the drug-resistant bacteria and negative impact of chemicals on the environment should be minimized. The present invention proposes an environmentally friendly method, without chemical pesticides, of plant disease control using novel jumbo phage which is isolated from organically farmed soil.
Inquire About This Product
basic information
For details, please contact us or refer to the PDF.
Price range
Delivery Time
Applications/Examples of results
For details, please contact us or refer to the PDF.
catalog(1)
Download All CatalogsCompany information
The revenue generated from technology transfer is reinvested into universities and researchers as new research funding, which is used to create further research outcomes. To ensure the smooth operation of this cycle, known as the "Intellectual Creation Cycle," we will actively promote technology transfer. The types of seeds we handle include patents, know-how, databases, and programs. We have established a collaborative framework by concluding basic technology transfer agreements with the following universities (as of June 1, 2025): - Tohoku University - Hirosaki University - Iwate University - Akita University - Fukushima University - Yamagata University - Tohoku Gakuin University - Iwate Medical University - Fukushima Medical University - Aizu University - Miyagi University - Hokkaido University - Muroran Institute of Technology - Showa Medical University